Creating an MSO
Intended audience: ANALYSTS DEVELOPERS ADMINISTRATORS
AO Platform: 4.3
Overview
An MSO, short for Managed Semantic Object, is a node in the Ontology representing a real-world object digitally through a combination of data properties and metadata that gives the data context, additional qualities, and relationships with other objects.
An MSO can be created on one of three ways:
Using the Ontology Discovery option in the Ontology Composer - this is generally the recommended way of creating MSOs when an Ontology is first created due to the automation involved. Using the Ontology Discovery wizard will also allow an MSO to be created where the MSO Properties can be mapped to different data sources within a single MSO. This option is typically used in Federated Data use cases. See Ontology - Federated Data.
Using the Add MSO option in the Ontology Composer - an MSO is created using the Add MSO wizard that leads the user through a series of steps to create the basic MSO, including selecting a data source as the key starting point. This is the process described in the rest of this topic. The Add MSO wizard only allow a single data source to be mapped to the MSO Properties created.
Using the Pipeline Composer - an MSO can be attached to a Pipeline as a Sink - which means that the data structure output from the Pipeline (whatever data Sources and Transformations are involved) will be stored as an MSO.
On the MSO page, click the “+” icon to open the Create MSO wizard as described below.
Add MSO Wizard
Start
On the first page of the wizard, users can select from available data sources, including:
Databases, such as Google BigQuery, Apache Hive, PostgreSQL, Snowflake, CrateDB, Apache Cassandra, Microsoft SQL Server, SQL Server Analysis, Azure Synapse Analytics, Azure Data Lake Storage, Trino, Apache Druid, Oracle, MySQL, SAP S/4 HANA, Amazon Redshift, Jira, Databricks, and Salesforce.
Files, such as CSV, TXT, Excel/Large Excel, Shape, XML, and GeoJSON.
Other data sources, such as MongoDB, Elasticsearch, and Solr.
Pipelines - which is a special kind of data source created separately with access to any available data source in the Pipeline Composer, and where data may have undergone transformations.
Blank - which allows users to manually specify properties of a new MSO independent of any data source.
Click the Next button to move to the next page.

Data Source Details
On the Data Source Details page in the wizard, the user can populate the required and some optional fields to connect to the selected data source.
For SQL Databases, service details, such as access URL, account with credentials and other mandatory properties, must be preconfigured in the Admin solution for the associated dropdown properties to be available and selectable.
Click Select Table to select from available Tables in the Metadata Cache. See Adding Schemas and Tables to Metastore Cache for details.
For File-based data sources, the user can either upload from a local system or select from already uploaded files from the AO Platform data source repository.
For Cloud-based data sources, the user can select from already uploaded files from available Cloud Storage services. Such Cloud Storage services must be preconfigured in the Admin solution with details such as access URL, account with credentials, and other mandatory properties, for the associated dropdown properties to be available and selectable.
Click the Next button to move to the next page.
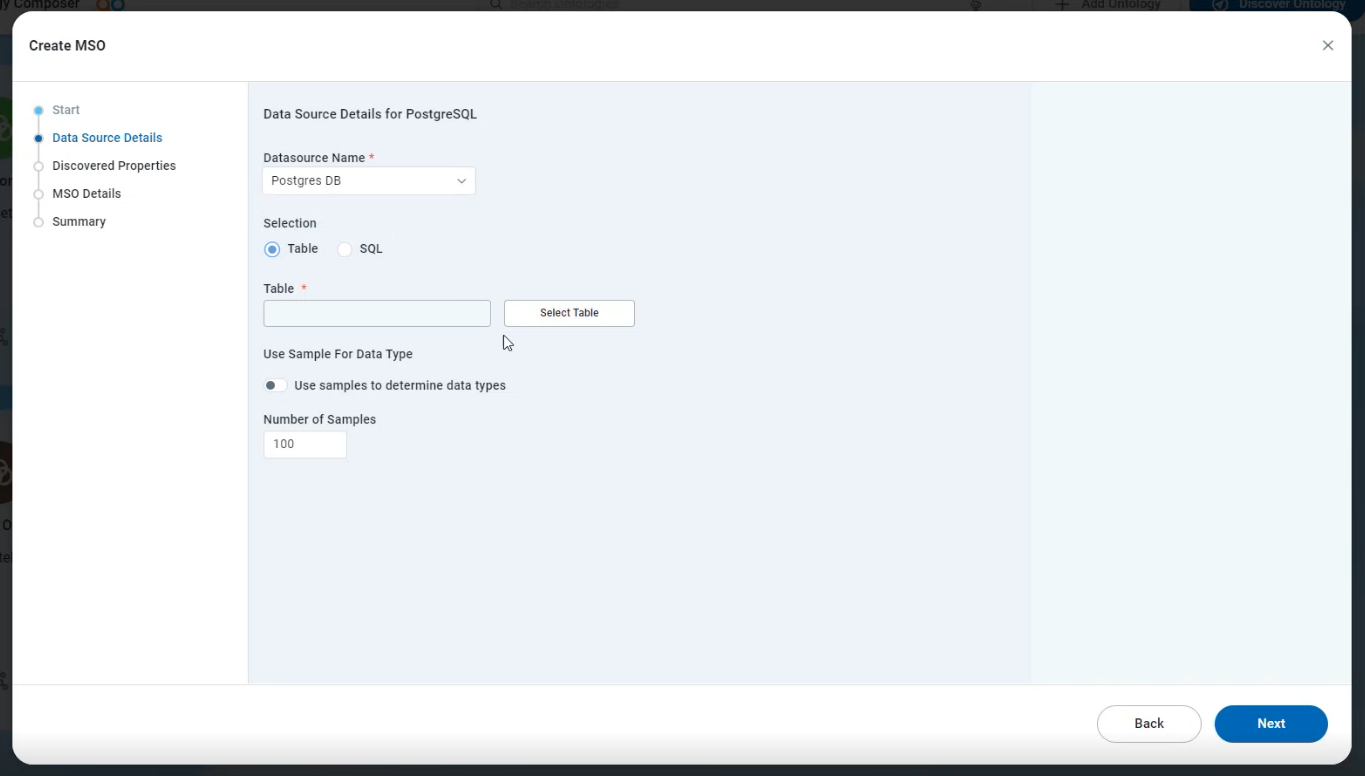
Discovered Properties
On the Discovered Properties page in the wizard, the user will be able to see:
The data structure is retrieved from the selected data source - on the MSO Properties tab.
On the MSO Properties tab, the user can click the values of any MSO Field Name, MSO Display Name, and Data Type to make changes if the auto-creation process didn’t get it quite right.
A representation of the actual data values - on the Samples tab.
Click the Next button to move to the next page.
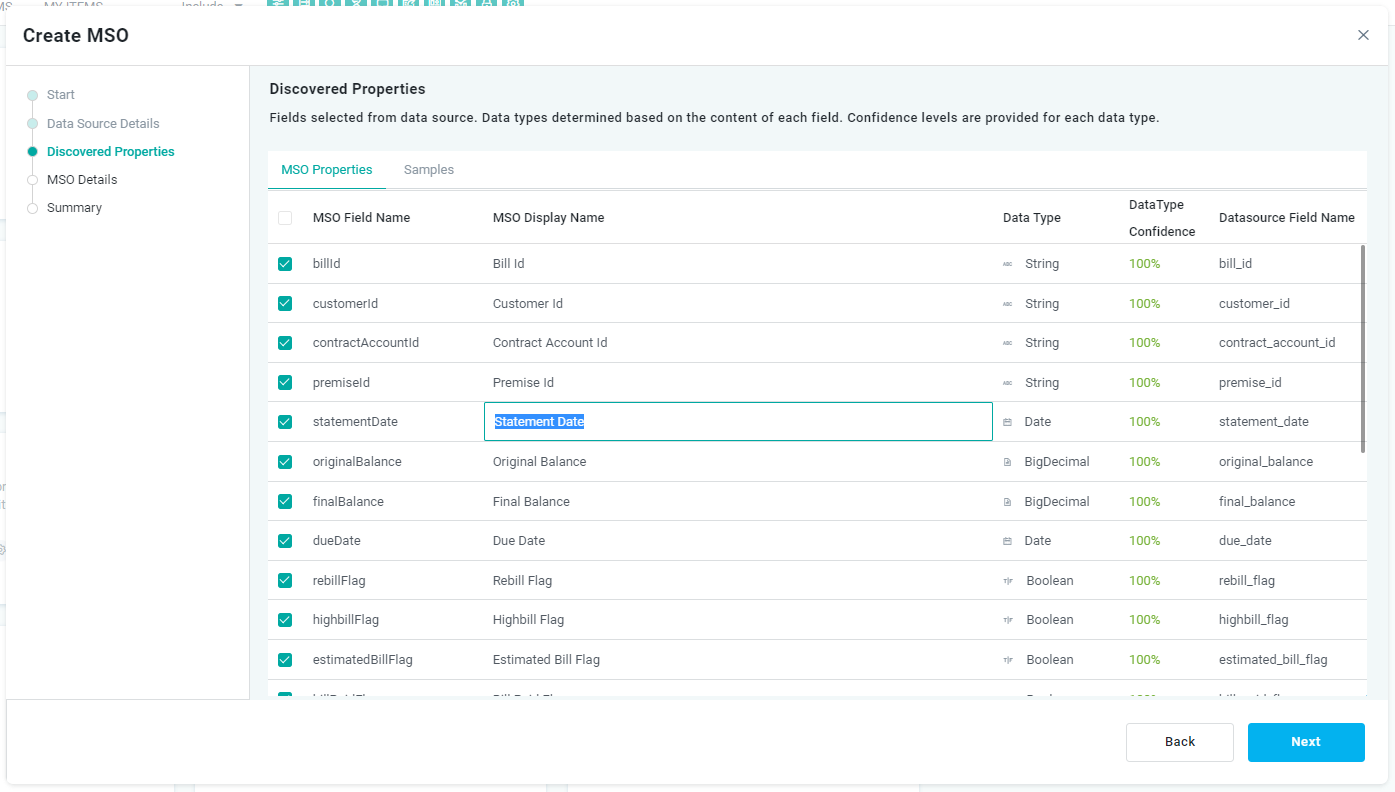
MSO Details
On the MSO Details page in the wizard, the user can provide some final general MSO properties, such as the MSO Name, Domain, Ontologies, Description, and finally the desired Source Type for the data source itself.
The Source Type determines the “readiness” of the data source if the data resides in a Cloud Storage environment and the user wants to take advantage of different readiness/cost options. Options include: Hot, Warm, and Cold.
The user can finally select/deselect the field properties available from the data source if only a subset of the properties is required.
Click the Next button to move to the Summary page.
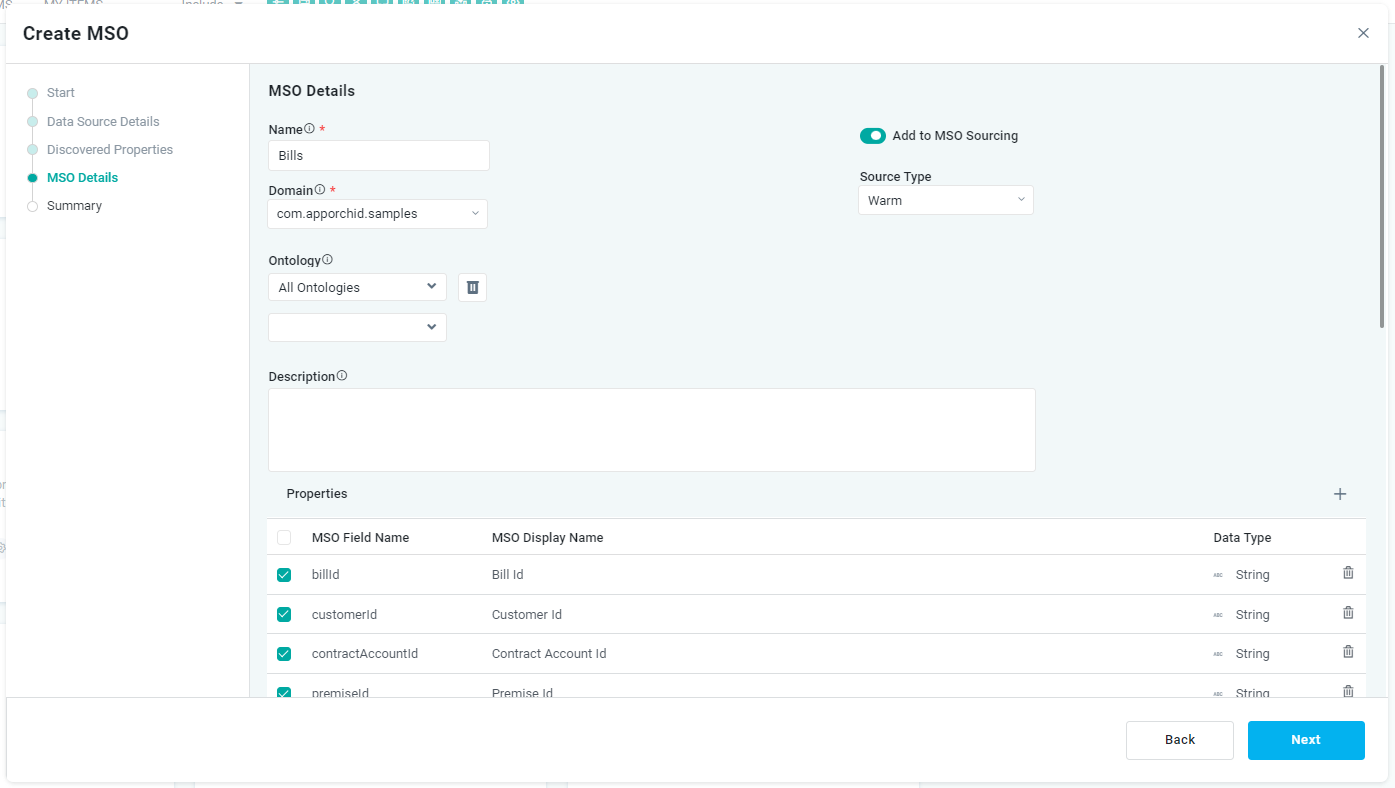
Summary
On the Summary page, the user will see a visual representation of the MSO that has been created from the data source and its properties. Use the menu options to adjust the visual representation. See Ontology Viewer for details.
Click the Finish button to create the MSO.
Once the Create MSO wizard has been finalized, the user is ready to configure additional MSO options. See Editing an MSO.
