Creating a Model
Intended audience: DATA SCIENTISTS DEVELOPERS ADMINISTRATORS
AO Platform: 4.3
Overview
This topic describes the Machine Learning (ML) Model creation workflow.
The Model Composer Creation Workflow
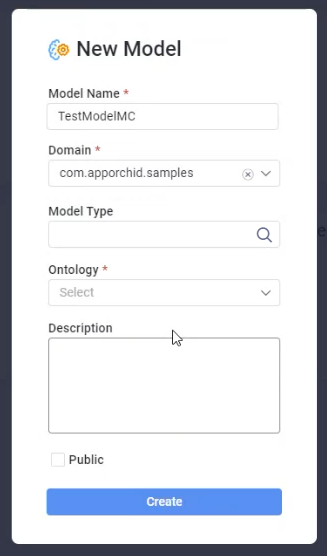
Creating a Model is done by selecting Add New on the Model Composer landing page. The following properties are available:
Model Name - provide a meaningful name for the ML Model being created.
Domain - select from available Domains in the dropdown.
Model Type - this is the initial selection of the type of models to be trained. Click to open a Search dialog. See details Creating a Model | Model-Types-with-Use-Case-Examples.
Ontology - select one or more Ontologies that this ML Model can be used with.
Description - provide a full description of the ML Model being created.
Public - check the checkbox to make the ML Model available to other users of the Model Composer.
Model Types with Use Case Examples
Icon | Model Types | Description | Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Clustering (unsupervised learning) | Clustering is an exploration technique used to categorize data into meaningful groups or “clusters” without any prior information about the cluster credentials (so, it is solely based on their internal patterns). The cluster credentials are determined by similarities of individual data objects and their differences from the rest of the objects. |
|
 | Classification (supervised learning) | In this technique, the input data is labeled in accordance with the historical data samples and is then manually trained to identify particular types of objects. Once it learns to recognize desired objects, it then learns to categorize them appropriately. To do this, it has to know how to differentiate between the acquired information and recognize optical characters/images/binary inputs. |
|
 | Regression (supervised learning) | This technique first identifies the patterns in the sample data and then calculates or reproduces the predictions of continuous outcomes. To do that, it has to understand the numbers, their values, their correlations or groupings, and so on. |
|
 | Binary Classification - Bayesian | Binary Classification using Bayesian methods is a powerful technique for predicting and categorizing data into two distinct classes. It leverages a probabilistic framework, which means it provides probabilities for each class, allowing us to quantify uncertainty in our predictions. This approach also enables us to incorporate prior beliefs or knowledge about the data, making it more flexible and informative. |
|
 | Multi Classification - Bayesian | Multi-Class Classification using Bayesian methods is a powerful technique for categorizing data into multiple classes or categories. Unlike binary classification that deals with two classes, multi-class classification involves predicting one class among several possible classes. Bayesian techniques provide a probabilistic framework, enabling us to model uncertainty and incorporate prior beliefs about the data. |
|
 | Regression - Bayesian | Regression using Bayesian methods is a powerful approach to predict continuous outcomes based on input features. Unlike traditional regression techniques, Bayesian regression provides a probabilistic framework, allowing us to model uncertainty in our predictions. It incorporates prior beliefs or knowledge about the data, making it flexible and informative. |
|
 | Time Series - Bayesian | Time Series Analysis using Bayesian methods is a powerful approach to model and forecast data that varies over time. It provides a probabilistic framework, allowing us to capture uncertainty and make predictions with confidence intervals. Bayesian time series models are well-suited for dealing with noisy and dynamic data, making them valuable in various applications. |
|
After clicking the Create button, the user is sent directly into the Editing a Model workflow.
