Intended audience: Data scientists developers administrators
AO Platform: 4.3
Overview
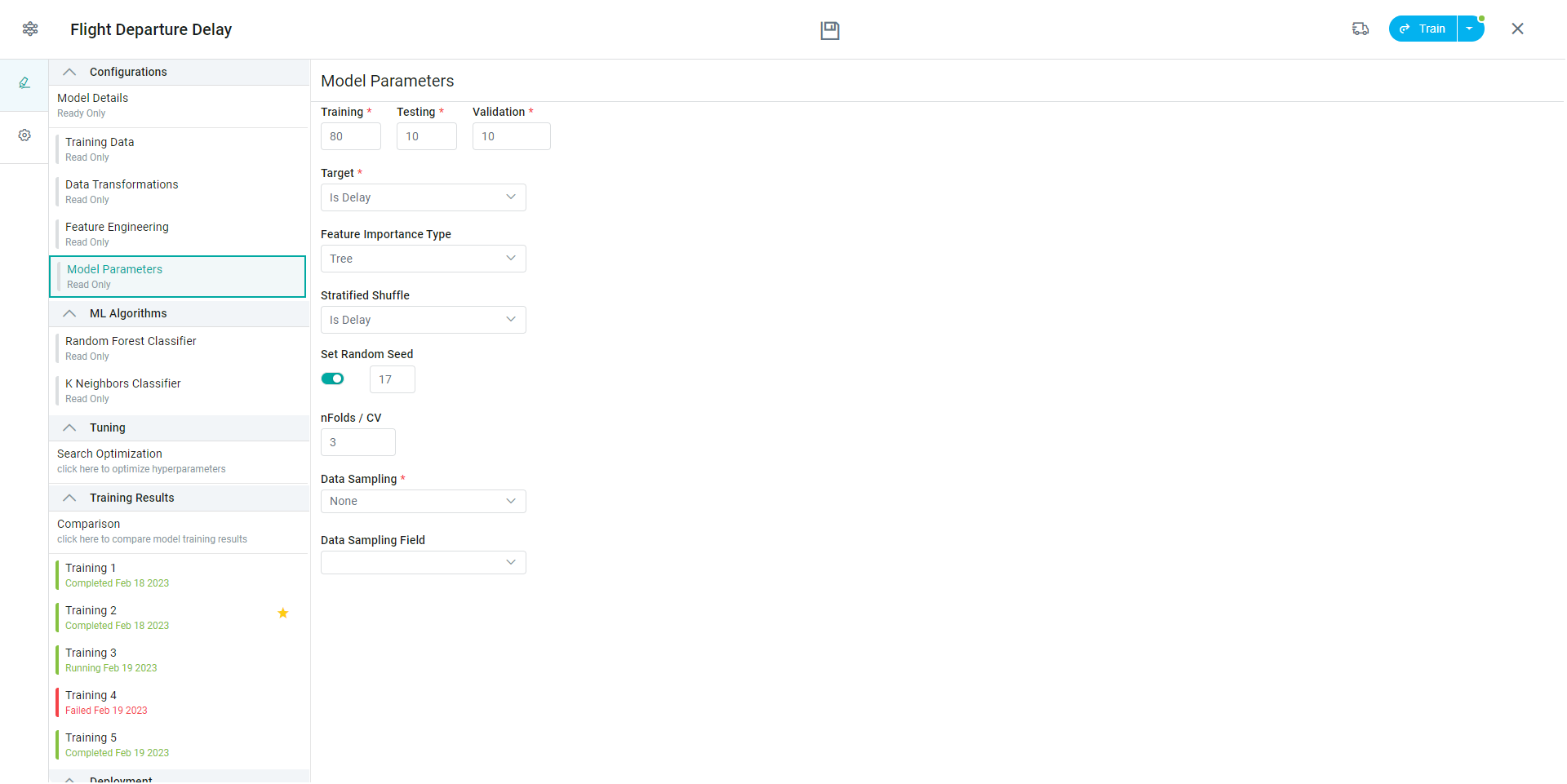
Properties
|
Label |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Training |
This percentage of the Training Data will be used for training the Models. The result will feature metrics based on this percentage. |
|
Testing |
This percentage of the Training Data will be used for testing the Models. |
|
Validation |
This percentage of the Training Data will be used for validating the Models. |
|
Target |
Use this dropdown to select the target field from the data source for the model. |
|
Feature Importance Type |
A technique for assessing data towards the Target. Includes the following options in dropdown:
|
|
Stratified Shuffle |
Provides train/test indices to split data in train/test sets. This cross-validation object is a merge of StratifiedKFold and ShuffleSplit, which returns stratified randomized folds. The folds are made by preserving the percentage of samples for each class. |
|
Set Random Seed |
The seed value is a base value used by a pseudo-random generator to produce random numbers. The random number or data generated by Python’s random module is not truly random; it is pseudo-random (it is PRNG), i.e., deterministic.
|
|
nFolds / CV |
K-fold cross-validation is used to validate a model internally, i.e., estimate the model performance without having to sacrifice a validation split. Also, you avoid statistical issues with your validation split (it might be a “lucky” split, especially for imbalanced data). Good values for nfolds are generally from 5 to 10, but keep in mind that higher values result in higher computational cost. |
|
Data Sampling |
The Imbalanced classification problem happens when there is a skew in the class distribution of our training data. An approach to combat this challenge is Random Sampling. There are two main ways to perform random resampling, both of which have pros and cons:
In other words, Both over sampling and under sampling involve introducing a bias to select more samples from one class than from another, to compensate for an imbalance that is either already present in the data, or likely to develop if a purely random sample were taken. |
|
Data Sampling Field |
Select the field for which Data Sampling will be executed. |
Contact App Orchid | Disclaimer
